Integral method of training
Integral method
This section explains what is the comprehensive method of training.
Introduction
At the beginning of the modern football conditioned by the idea of getting "fresh" parties trained relatively little (low training volumes). In fact, somatotype of player was very different to the existing nowadays.
Later it gained relevance the physical preparation and stormed the football using systems of training based primarily on athletics. So the integration of the physical work was carried out non-specific.
Currently there is a trend to the ball again to be the element central on which turn all the session of training and many coaches called to this method: "training integrated" by the mere made of include the ball in all time.
However, the comprehensive training requires more complex that simply include a balloon in all exercises. It goes beyond to try to approach training as much as possible to the competition, using a scientific method by means of which should be:
- Objectively assess the intensity of the work carried out with ball using scientifically validated methods.
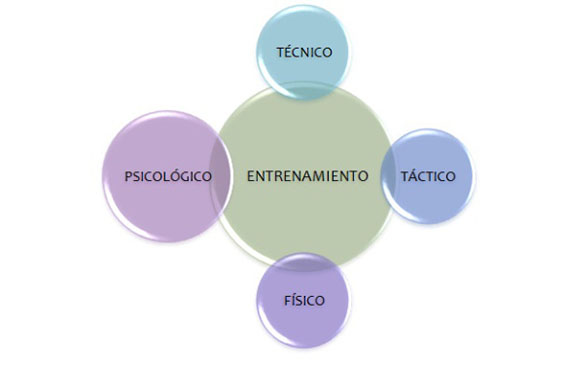
- Get the physical, technical, tactical and psychological objectives in each fiscal year.
And it is that not everything is invented in football, on the other hand, there is ample scope for research and innovation that open us an infinite number of possibilities to experience to follow the scientific method as used in other areas of the knowledge.
Definition of the Integral method
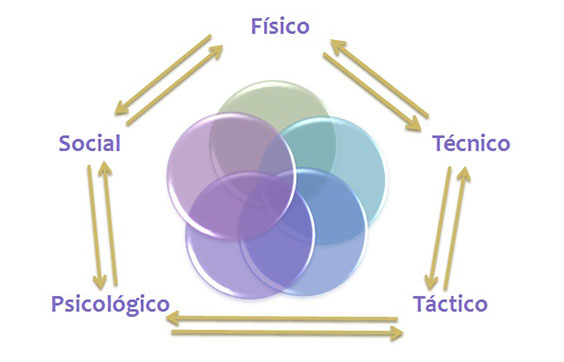
By comprehensive training, we understand all those simplified game situations by means of which we try to develop technical, tactical, physical and psychological aspects that are required in the competition.
This training model aims to establish a methodology of work as objective as possible that will allow us to achieve the highest level of performance taking the ball as a primary means of work.
Aspects to be considered in any training method
At the time of consider any task to develop within the session of training will have that determine clearly the following aspects:
- Purpose it is intended to develop.
- To whom it may concern.
- Media to use.
- Most appropriate method to use.
In the measure that we are going to use more specific tasks or exercises must consider:
- Technical, tactical, physical and psychological aspects of football.
- Characteristics of the players.
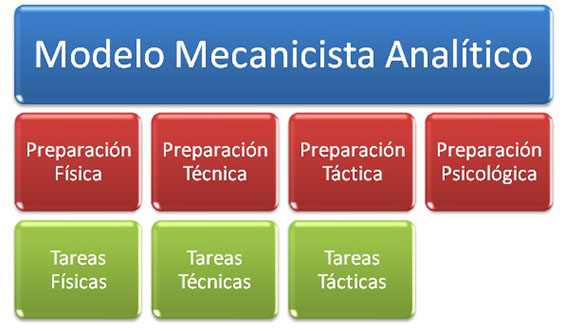
Analytical methodology
Is the method more used to the date. Both the performance of the player and the game itself is observed as the sum of multiple performance: physical, technical, tactical and psychological.
Each yields is trained separately by independent training.
Sets a task for each goal to ignore the information of efforts made during the development of this task. Also leave in the background the psychological aspect, which is practically not working or so is made in an isolated manner without the involvement of the footballer.
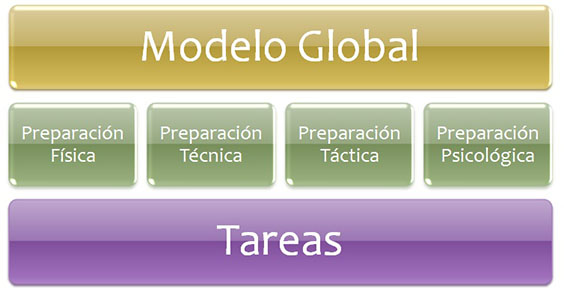
Overall methodology
The performance of the footballer is completed from a global perspective and training exercises are conducted through the simultaneous and integrated development of the technical, tactical, physical and psychological factors.
Taking into account this view the concept of form ("being in shape") adopts a new global perspective and integrating that moves away from the purely physical component of the term. The concept of psychological status, appearance of the human being as a whole complex, gains protagonism and is integrated into the training as one more element.
The so-called "integrated training" frame within this global methodology of training as opposed to the analytical methodology.
Types of exercises according to the specificity
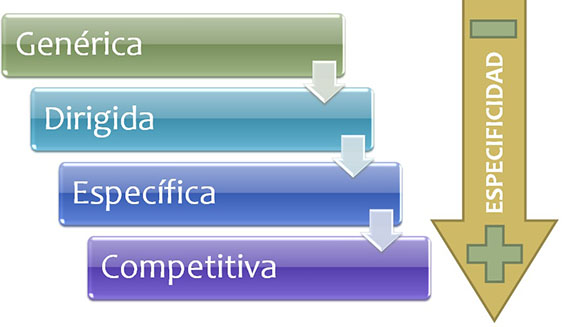
We will progressively go from more generic to more specific exercises although in our "integrated training", we will only use the most specific exercises.
To develop this classification took into account two fundamental aspects:
- Objective pursued by the exercise.
- Medium used for the development of the exercise.
From least to greatest specificity:
- Generic exercise: both the objective and the means used for their development are generic. For example, the continuous race is a generic means for improving aerobic capacity (generic physical attribute).
- Exercise addressed: one of those factors is specific and the other generic. For example, confrontation of two teams in the Middle field that they have to keep possession of the ball (specific medium) for the development of aerobic capacity (generic physical attribute). Another example would be to carry out an extensive interval (between generic) for the improvement of the aerobic power (specific physical quality).
- Exercise specific: when those two factors are specific. For example: 3 series of 5 minutes of 4 against 4 more goalkeepers in 40 × 25 meters (medium specific) for the improvement of the aerobic power (specific physical quality).
- Competitive exercise: when two factors are specific and there are psychological elements (stress, pressure, anxiety...) which are close to the real situation of competition.
The sports ability to obtain optimum performance not only depends on the level of development of factors such as the physical condition, but relates and expands with other fields such as tactical, technical, psychological and social capabilities. Therefore, we can say that in competition performance depends on multiple abilities and complex synergies between them.
Then we'll discuss what factors we must take into account when planning a training:
- CONDITIONAL factors: Related to energy processes are traditionally classified in strength, endurance, speed and flexibility. It are not an end in themselves but rather a means.
- DRIVING factors: Related to quality and the adjustment of the drive elements. They are closely related to the technical aspect.
- INFORMATIONAL factors: Related to the treatment of the information. Players are constantly processing data based on: I) the targets to get at the tactical level. (II) the perception of the changed environment. (II) the search for best decision footage.
- PSYCHOLOGICAL factors: Among which we must highlight: motivation, self-control, intelligence - mental ability, cohesion team, perception of success, self-confidence, anxiety, attention, concentration, self...
- ENVIRONMENTAL factors of the team: characteristics of the club, direction model, means that are available, working conditions...
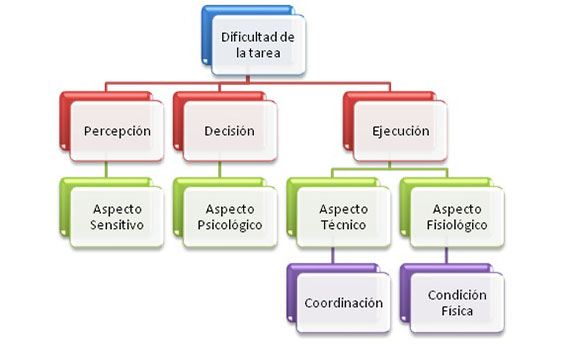
The actions of the game respond to some parameters more or less standardized biomechanical who are conditioned by factors as detailed and that require a constant adaptation to the changed competitive situation. In the majority of occasions, decisions taken by the player and the correct perception of reality will make the execution of the action has or not helpful. Therefore, when evaluating the contents of the training we consider exercise to be carried out from a triple point of view:
- Perceptive.
- Decision-making.
- Execution.
Primary and secondary objectives
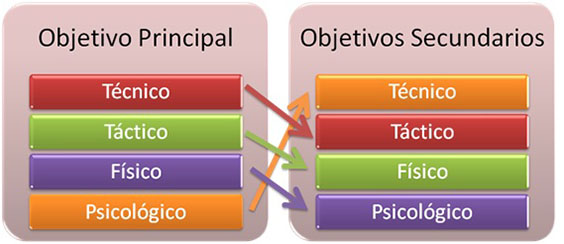
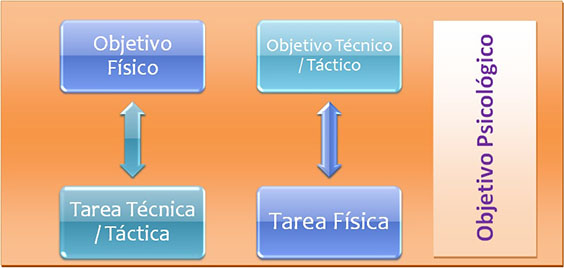
When choosing exercises for each training session not only we will take into account the technical aspects - tactical that traditionally have been considered determinant in athletic performance, but you will have to evaluate both the physical aspects as psychological that each exercise involves, although for establish the objectives of the session will give some priority to them components technical and tactical.
But since you are talking about a training integral of this work must have multiple addresses. I.e., not always depart from the improvement of a physical quality and the subsequent election and implementation of specific exercises suitable for the development of the same. But in the majority of cases we will depart from a technical or tactical goal that we want to work at all times and both physical and psychological content of the exercise will be something that will determine us the choice of the same. Although we also starting from the interest in improving a particular psychological aspect and the subsequent election of specific exercises suitable for development with independence for also technical aspects, work simultaneously tactical and physical.
Regardless of the initial criteria which mark us the choice of exercise or another, all of them must adapt in its physical component to microcycle in training that we find on the basis of the general planning of the season.
Once chosen the main objective and the task which is intended to achieve this objective, a multi-directionality must be given in the analysis.
Therefore, the approach may be from different perspectives:
- Point of view of the physical trainer (eminently physical aspects).
- Point of view of the coach (eminently technical and tactical aspects).
- Point of view of the psychologist (mainly psychological aspects).
- Global point of view.
Then we will develop briefly each of them:
- From the point of view of the preparer physical: choice of the exercise starting from objective physical, not valuing many times or them aspects technical-tactical or them psychological. The burden of physical exercise is assessed to perform.
- From the point of view of the trainer: choice of exercise from objective technical - tactical, unrated developed neither physical nor psychological aspects. Neither estimated the burden of physical exercise performed.
- From the point of view of the psychologist: choice of exercise or the dynamics of group from only psychological objectives.
- From a global point of view: choice of the exercise from the target tecnico-tactico who want to develop, but by also selecting it within a physical condition and psychological set.
In the integral method, the classification and selection of exercises will be held from the global point of view.
Creation of a database of exercises
In our case, the classification and selection of exercises will be only from the global perspective from scratch creating a database in Access format or similar which will include including those exercises which, according to our criteria, consider more ideal.
Once you create the database you can search those exercises that meet conditions for us elected in brief and simple.
When making a selection we will be filtering exercise based on the criteria that we go by choosing. For example:
- Filter in first place those in which is work the aspect tactical of: "improvement of them supports"
- Then the retrieved total of exercises, we will make a second filter with those that improve the physical condition of "aerobic power".
- Obtained exercises, we will make a third filter in which we will include a psychological aspect that we want to work, as for example "group cohesion"
Once the 3 filters, we will obtain a number "x" of exercises that we will choose one.
You can make as many filters as you want, but if you do not have a wide and varied database, it is possible to not find sufficient exercises to perform very specific searches. For this reason, do attempt to introduce the greatest possible number of exercises since more specificity, the greater the quality of the training.
The basic criteria that we must enter into the creation of our database are as follows:
- Name of the exercise.
- Assessment of the exercise.
- Main tactical objective.
- Main technical objective.
- Objective physical main.
- Main psychological objective.
- Secondary tactical objective.
- Objective technical secondary.
- Secondary physical objective.
- Secondary psychological objective.
- 1Superficie (dimensions of space in metres. Example: 10 × 8 meters).
- No. players (the number of players involved. Example: 9 players).
- Time (the total duration of the exercise. Example: 10 minutes).
- Description (will explain briefly what is the exercise).
- Graph (a graph which is observed visually exercise is included).
- Comments (include comments that the coach deems appropriate of the type: warnings, aspects to take into account possible variants...)
Depending on the degree of specificity that we want to obtain, will introduce other variables of type: number of repetitions, number series, time, heart rate intensity, lactate levels...
When it comes to include a variant of a same exercise, you must enter in the database as a new exercise when introduced variations imply a change of the technical, tactical, physical or psychological objective. For example, in an exercise that has as main objective the best control oriented, if we introduce the condition that you can only play a touch as Variant, obviously no longer can maintain is aimed at technical oriented control. Emerging a new target tactical as it is the speed in the game.
Obviously, a same exercise can have several objectives, technical, tactical, physical or psychological, although there will always be a main objective, which is to which we will have to introduce in the column's main objectives. Introducing the secondary objective in the column designed for this purpose. When a same exercise has several main objectives or several secondary objectives, you will need to enter the exercise as if it were a new exercise, using the same name followed by the number 2,3,4... depending on the number of times that is introduced that same year.
However, in the database not the General and the specific objectives should be included only. I.e. in whole possession is going to necessarily work pass and control alike, but depending on which has the exercise (small space, 4 goals, play a touch, 8 5...) some tactical aspects will work specifically and certain physicists. As well, when introducing the exercise to the database you don't need include obvious as the pass or control technical objectives.
Online as indicated above and with the aim of increasing the quality of our database, we will have to take into account other aspects:
Base conditional of the system, represented by parameters physical of the type:
- Time of duration of the effort.
- Intensity.
- Recovery time.
- Number of replicates per series.
- Number of series.
- Within the columns: "main physical objective" and "secondary physical objective" are included the main or secondary technical aspects that seeks to improve each year.
- Co-ordinating or technical elements to insert into the exercise. Inside the columns: "objective technical main" and "objective technical secondary" is include them aspects technical main or side that aims to improve each exercise.
- Cognitive or tactical elements to insert into the exercise. Within the columns: "main tactical objective" and "target secondary tactician" are included the main or secondary tactical aspects that aims to improve each year.
- Psychological elements to insert. Within the columns: "psychological objective" and "secondary psychological objective" are included the main or secondary psychological aspects that seeks to improve each year.
Planning of training
When implementing the planning the first aspects to consider are:
- Objectives.
- Potential of the team.
- Competitive calendar.
The steps to follow are:
- Select the schedule type.
- Select the means and methods.
- Objectify and rank the exercises that we use (database).
- Define the objectives of the week: flaws and virtues of our team; and deficiencies and virtues of the rival.
- Select media for the fulfilment of the objectives on the basis of the results of the analysis of the previous point.
- Organize media according to the expected load (ATR planning or classical) dynamics.
- Daily analysis and load adjustment planned if necessary.
- Analysis of the behavior of the team during the competition weekend.
We must analyze what have been the aspects to improve during the course of the competition (the party of the weekend). We will have to go performing a methodical analysis with help of all observational media that may be within our reach. For example:
(to) Technical deficiencies - defensive tactics observed:
- Difficult to replicate in a coordinated manner to the counterattack of the opposing team.
- Difficulty to reach the pressure over the mean Center of the opposing team.
b) Technical shortcomings - offensive tactics observed:
- Slowness of players located behind the ball when it comes to joining the counterattack.
- Walking by the bands.
c) Physical deficiencies observed:
- We have noticed the team physically very tired in the last 15 minutes of matches.
d) Psychological deficiencies observed:
- The team is often emotionally come down after conceding the first goal in the first 20 minutes of the match, running out of capacity to react until entrance the second part.
Similarly, we will make an analysis of the virtues of our team to enhance the strong points, although we will focus most of the time training on the improvement of deficiencies.
Subsequently make available media (videos, observation of recent matches, technical reports...) analysis of the opposing team:
(to) Technical virtues - defensive tactics observed:
- § Solid defense with an average Center that balances well the team and a defensive line that barely lost the safe order by the band left, although by this band has more offensive arrival.
b) Technical virtues - offensive tactics observed:
- Good game by bands, mainly on the left side. The right wing is more predictable.
c) Observed physical virtues:
- The line from the center of the field in general has explosive speed, especially when he joins offensive work.
d) Observed psychological virtues:
- The team is very United and they look very cohesive.
- They have great ease when it comes to overcome adverse situations thanks largely to their captain, which exerts an undisputed leadership.
Similarly observed defects would be scanned to detect its weaknesses. Although we will focus especially on neutralizing its virtues.
Both in the analysis of our team and in the analysis of the rival we must focus on the virtues and defects more important since it would not be very realistic to try to work during the week the improvement of more than two or three specific aspects.
Once the analysis of strengths and weaknesses of both teams we would spend to the location of the week within the global physical planning. For example:
Assuming the type ATR planning (accumulation - transformation - realization), we find ourselves in microcycle IV, from the least of preparation with the following physical objectives:
- Capacity - aerobic power.
- Lactic power (strength - speed).
- Explosive strength.
- Gestural speed.
The first thing we have to do is reset the physical work of the week to physical deficiencies observed. In our example, we have observed that the computer has a considerable physical downturn in the final minutes of matches, so it would be convenient to reduce the intensity and volume of the work of the aerobic capacity to try to get more fresh to the next party.
As for the planning of the technical work - tactician of the week, based on the analysis previously carried out in our example, would read as follows:
- Development and refinement of orientation changes to short to take advantage of the numerical superiority in midfield.
- Improved counterattack with incorporation of midfielders at auction.
- Perfecting reduction in defense areas.
- Movements from the side.
Then we'd go choosing from our database exercises that best suit the technical and tactical objectives set, trying to choose those exercises that fulfilling these, the marked to improve the deficiencies identified at this level psychological objectives also conform.

from Guatemala Wishing you better hope you post exercises tactful technique thanks
Very good explanation, you may also add that this type of training is used by some trainer staff in disciplines such as Crossfit that are based on functional movement, this means that your body was designed to do this kind of exercises.